ENCODE4 Histone ChIP-seq Data Standards and Processing Pipeline
Assay overview
ChIP-seq is a method used to analyze protein interactions with DNA. ChIP-seq combines chromatin immunoprecipitation with DNA sequencing to infer the possible binding sites of DNA-associated proteins. The ENCODE consortium has developed two analysis pipelines to study two different classes of protein-chromatin interactions. The histone ChIP-seq pipeline, described here, is suitable for proteins that associate with DNA over longer regions or domains. A typical target would be a histone protein or a specific post-translational histone modification.
The transcription factor ChIP-seq (TF ChIP-seq) pipeline is suitable for proteins that are expected to bind in a punctate manner, and is available here.
Updated July 2020
Pipeline Overview
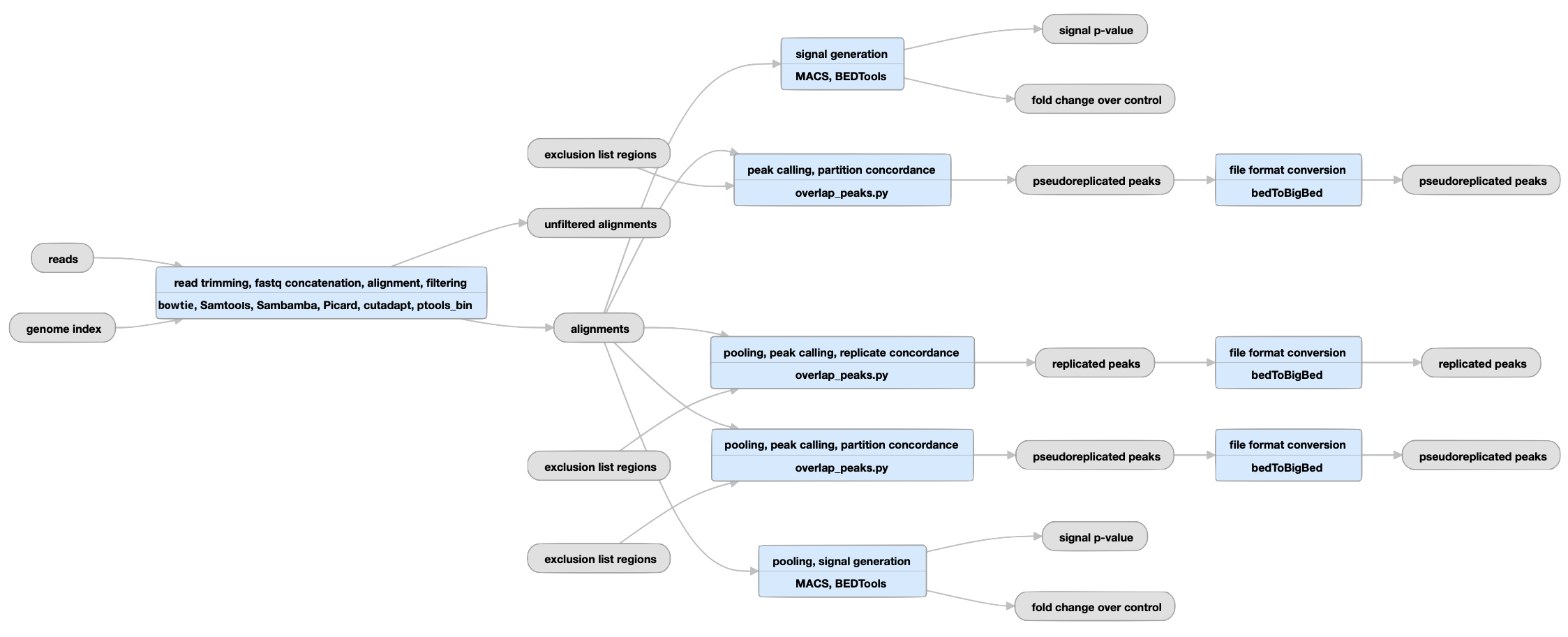
The ChIP-seq histone pipeline was developed as a part of the ENCODE Uniform Processing Pipelines series. The ENCODE consortium has developed two analysis pipelines to study the different classes of protein-chromatin interactions. Both ChIP-seq pipelines share the same mapping steps, but differ in the methods for signal and peak calling and in the subsequent statistical treatment of replicates. The full ChIP-seq pipeline code is available on Github.
The histone analysis pipeline can resolve both punctate binding and longer chromatin domains that are bound by many instances of the target protein or target modification. The output of the histone ChIP-seq pipeline is suitable as input to chromatin segmentation models which seek to classify chromatin regions into functional categories.
Replicated experiments
View the current replicated histone pipeline instance.
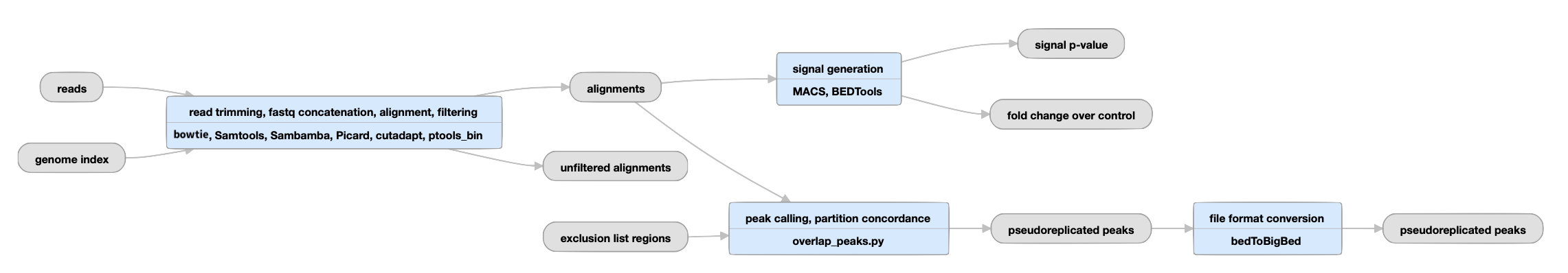
Uneplicated experiments
View the current unreplicated histone pipeline instance.
Back to the top
Inputs:
| File format |
Information contained in file |
File description |
Notes |
| fastq |
reads |
G-zipped reads, paired-ended or single ended, stranded or unstranded. | Multiple fastqs from a single biological replicate or library are concatenated before mapping. Reads must meet the criteria outlined under the Uniform Processing Pipeline Restrictions. |
| fasta | genome indices | Indices are dependent on the assembly being used for mapping |
Outputs:
| File format |
Information contained in file |
File description |
Notes |
|
| bigWig | fold change over control, signal p-value | Two versions of nucleotide resolution signal coverage tracks. |
The signal is expressed in two ways: as fold-over control at each position, and as a p-value to reject the null hypothesis that the signal at that location is present in the control. |
|
|
bed and bigBed (narrowPeak) |
peaks |
Relaxed peak calls for each replicate individually and for both replicates reads pooled together. |
These peaks are thresholded to sample enough noise in the experiment for efficient statistical comparison of replicates in subsequent steps; as such, many false positives are expected to be present. They are not meant to be interpreted as definitive binding events, but are rather intended to be used as input for subsequent statistical comparison of replicates. | |
|
Replicated datasets only |
||||
| bed and bigBed (narrowPeak) | replicated peaks | The set of peak calls from the pooled replicates. |
These peaks are either observed in both replicates, or are observed in two pseudoreplicates. Pseudoreplicates are peak sets called on half of the pooled reads, chosen at random without replacement. |
|
|
Unreplicated datasets only |
||||
| bed and bigBed (narrowPeak) | pseudoreplicated peaks | The set of peak calls from two partitions, or "pseudoreplicates" |
In the "partition concordance" step, a similar "naive overlap" strategy is used to identify pseudoreplicated peaks across pseudoreplicates (instead of across true replicates). Pseudo-replicated peaks are peaks from the relaxed set that overlap at least 50% with peaks from both pseudoreplicates. |
|
|
Quality control metrics are collected to determine library complexity, read depth, FRiP score, and reproducibility. |
||||
References
Genomic References
View the human (GRCh38) and mouse (mm10) reference files used in this pipeline
Links and Publications
Find data generated by the histone pipeline for replicated experiments
Find data generated by the histone pipeline for unreplicated experiments
Explore all ChIP-seq related publications on the ENCODE portal
Back to the top
Uniform Processing Pipeline Guidelines
- The read length should be a minimum of 50 base pairs, though longer read lengths are encouraged; the pipeline can process read lengths as low as 25 base pairs. Sequencing may be paired- or single-ended.
- The sequencing platform used should be indicated. Different sequencing platforms might not be comparable. For example, replicates of HiSeq2000 vs. HiSeq4000 are different, and not comparable.
- Replicates should match in terms of read length and run type.
- Pipeline files are mapped to either the human (GRCh38) and mouse (mm10) sequences.
Back to the top
Current Standards (ENCODE4/ENCODE3)
Experimental guidelines for ChIP-seq and epitope-tagged ChIP-seq experiments can be found here.
- Experiments should have two or more biological replicates, isogenic or anisogenic. Assays performed using EN-TEx samples may be exempted due to limited availability of experimental material.
- Antibodies must be characterized according to standards set by the ENCODE Consortium. Please see the linked documents for histone modification and chromatin-associated protein standards (October 2016).
- Each ChIP-seq experiment should have a corresponding input control experiment with matching run type, read length, and replicate structure.
- Library complexity is measured using the Non-Redundant Fraction (NRF) and PCR Bottlenecking Coefficients 1 and 2, or PBC1 and PBC2. Preferred values are as follows: NRF>0.9, PBC1>0.9, and PBC2>10.
- The minimum ENCODE standard for each replicate in a ChIP-seq experiment targeting narrow marks and investigated as a transcription factor is 10 million usable fragments. The recommended value is > 20 million, but > 10 million is acceptable.
- The minimum ENCODE standard for each replicate in a ChIP-seq experiment targeting broad marks and investigated as a broad histone mark is 20 million usable fragments. The recommended value is > 45 million, but > 35 million is acceptable.
- Replicate concordance in ChIP-seq experiments is measured by calculating IDR values (Irreproducible Discovery Rate). ENCODE processed IDR thresholded peaks files should have both rescue ratio and self consistency ratio values < 2 is recommended, but having only one of the ratio values < 2 is acceptable.
- The experiment must pass routine metadata audits in order to be released.
Target-specific Standards
- For narrow-peak histone experiments, each replicate should have 20 million usable fragments.
- For broad-peak histone experiments, each replicate should have 45 million usable fragments.
- H3K9me3 is an exception as it is enriched in repetitive regions of the genome. Compared to other broad marks, there are few H3K9me3 peaks in non-repetitive regions of the genome in tissues and primary cells. This results in many ChIP-seq reads that map to a non-unique position in the genome. Tissues and primary cells should have 45 million total mapped reads per replicate.
| Broad Marks | Narrow Marks | Exceptions |
|---|---|---|
|
|
|
Previous Standards (ENCODE 2)
Data quality standards for ENCODE2 are outlined in ChIP-seq guidelines and practices of the ENCODE and modENCODE consortia.
- Experiments should have two or more biological replicates, isogenic or anisogenic.
- Antibodies must be characterized according to standards set by the consortium for ENCODE2 data.
- Each ChIP-seq experiment should have a corresponding input or IgG control experiment with matching run type, read length, and replicate structure.
- Library complexity is measured using the Non-Redundant Fraction (NRF) and PCR Bottlenecking Coefficients 1 and 2, or PBC1 and PBC2. Preferred values are as follows: NRF>0.9, PBC1>0.9, and PBC2>10.
- The experiment should pass routine metadata audits in order to be released.
Target-specific Standards
- For narrow-peak histone experiments, each replicate should have 10 million usable fragments.
- For broad-peak histone experiments, each replicate should have 20 million usable fragments.