ENCAB392AZR
Alternate accession: ENCAB386AXO
Antibody against Homo sapiens POLR2G
Homo sapiens
HepG2
characterized to standards
Homo sapiens
K562
characterized to standards with exemption
Homo sapiens
any cell type or tissue
partially characterized
- Status
- released
- Source (vendor)
- GeneTex
- Product ID
- GTX108874
- Lot ID
- 40023
- Characterized targets
- POLR2G (Homo sapiens)
- Host
- rabbit
- Clonality
- polyclonal
- Purification
- affinity
- Isotype
- IgG
- Aliases
- xiang-dong-fu:POLR2G
- External resources
Characterizations
POLR2G (Homo sapiens)
not submitted for review by lab
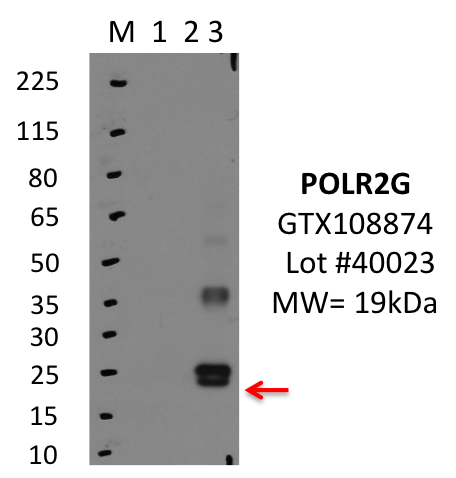
- Caption
- IP-WB analysis of K562 whole cell lysate using POLR2G specific antibody. Lane 1 is 2.5% of 0.5mg input lysate, lane 2 is 2.5% of supernatant after immunoprecipitation and Lane 3 is 50% of IP enrichment using rabbit polyclonal Anti-POLR2GpAb. This antibody passes preliminary validation and will be further pursued for primary and secondary validation.
- Submitted by
- Balaji Sundararaman
- Lab
- Gene Yeo, UCSD
- Grant
- U54HG007005
- Download
- GeneTex_GTX108874_40023_POLR2G.png
POLR2G (Homo sapiens)
HepG2K562
compliant
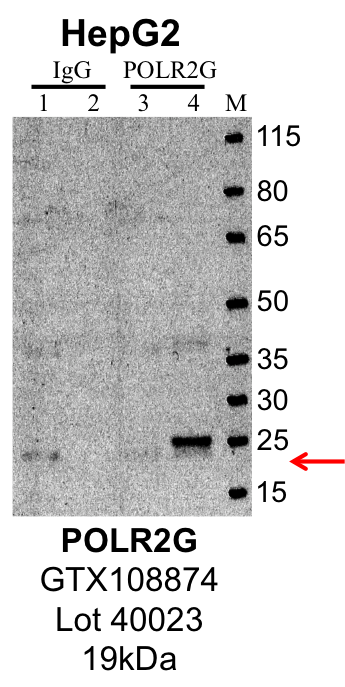
- Caption
- IP-Western Blot analysis of HepG2 whole cell lysate using POLR2G specific antibody. Lane 1 is 1% of twenty million whole cell lysate input and lane 2 is 10% of IP enrichment using rabbit normal IgG (lanes under 'IgG'). Lane 3 is 1% of twenty million whole cell lysate input and lane 4 is 10% IP enrichment using rabbit polyclonal anti-POLR2G antibody (lanes under 'POLR2G').
- Submitter comment
- This antibody was given and exemption for K562. The data was clean and the pattern is reliable.
- Submitted by
- Steven Blue
- Lab
- Gene Yeo, UCSD
- Grant
- U54HG007005
POLR2G (Homo sapiens)
compliant
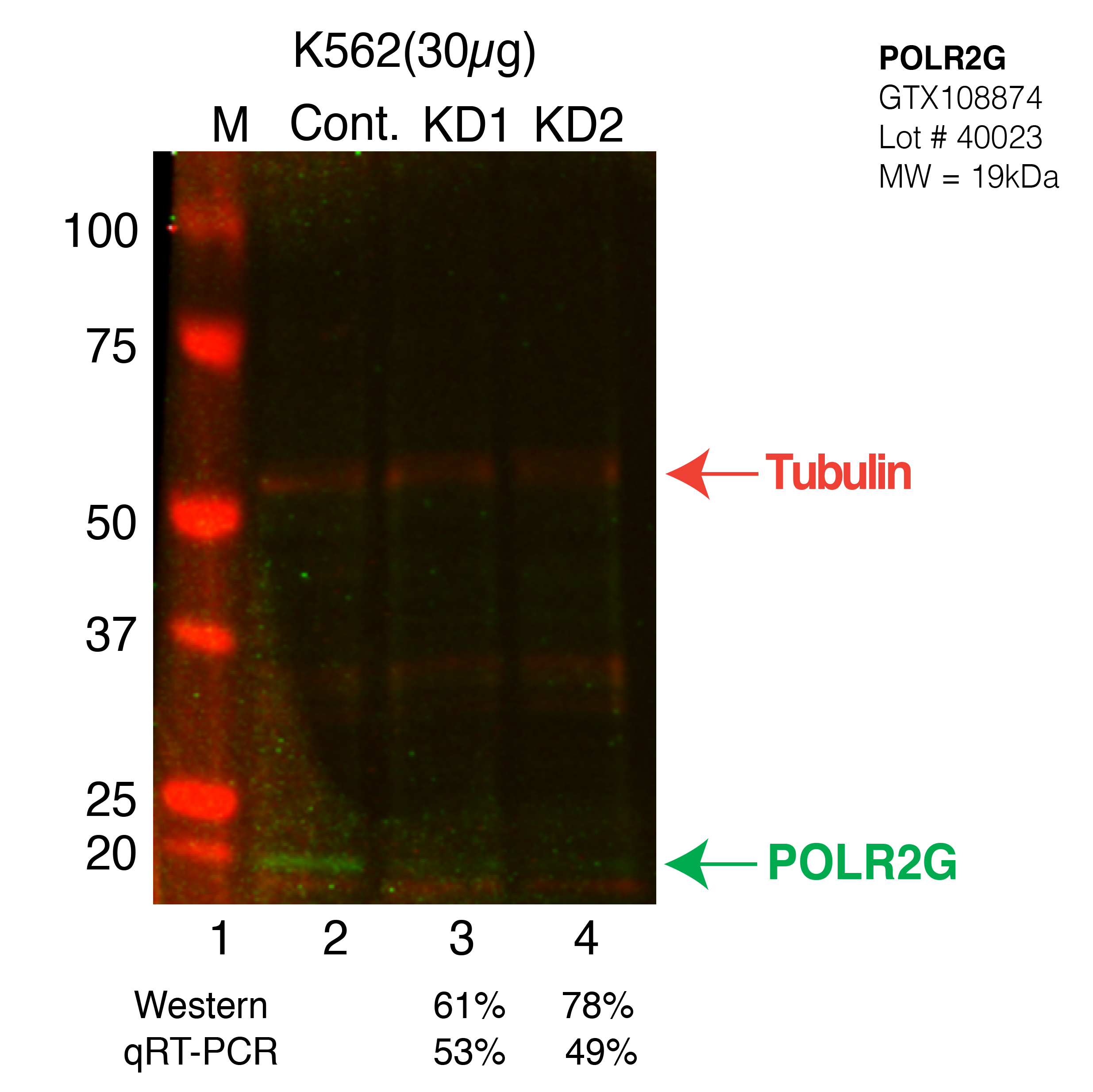
- Caption
- Western blot following CRISPR against POLR2G in K562 whole cell lysate using POLR2G specific antibody. Lane 1 is a ladder, lane 2 is K562 non-targeting control knockdown, lane 3 and 4 are two different CRISPR against POLR2G.POLR2G protein appears as the green band, Tubulin serves as a control and appears in red.
- Submitted by
- Xintao Wei
- Lab
- Brenton Graveley, UConn
- Grant
- U54HG007005
- Download
- POLR2G-CRISPR-K562.png