ENCAB770AFW
Antibody against Homo sapiens RAD21
Homo sapiens
K562
characterized to standards with exemption
- Status
- released
- Source (vendor)
- Abcam
- Product ID
- ab992
- Lot ID
- GR12668-7
- Characterized targets
- RAD21 (Homo sapiens)
- Host
- rabbit
- Clonality
- polyclonal
- Purification
- affinity
- Aliases
- michael-snyder:AS-31
- External resources
Characterizations
RAD21 (Homo sapiens)
exempt from standards
- Caption
- A new secondary characterization is not required as one exists for ENCAB000AKG which is a lot of the same antibody (ab992). The primary characterization (https://www.encodeproject.org/antibody-characterizations/2bf7eeee-2a31-46ba-956d-ecac94d65994/) of K562 for this lot shows the same banding pattern as the primary characterization (https://www.encodeproject.org/antibody-characterizations/a998bebe-57f7-4de9-8732-735fd07a8764) in K562 cell line for the lot ENCAB000AKG.
- Submitter comment
- This is a new lot of a previously characterized antibody ENCAB000AKG and we think no further characterization is necessary beyond the primary if the banding pattern is consistent with the old.
- Reviewer comment
- The banding pattern in K562 is consistent with that of the primary characterizations associated with old lot ENCAB000AKG so a new secondary characterization for the new lot is not needed.
- Submitted by
- Jessika Adrian
- Lab
- Michael Snyder, Stanford
- Grant
- U54HG006996
- Download
- ENCAB770AFW_secondary.png
RAD21 (Homo sapiens)
K562
compliant
- Caption
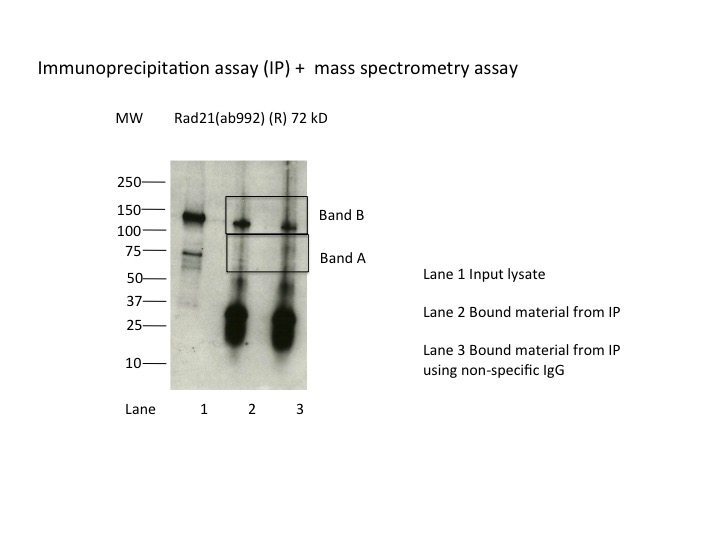
- Immunoprecipitation was performed on nuclear extracts from the cell line K562 using the antibody ab992. Lane 1: input nuclear lysate. Lane 2: material immunoprecipitated with antibody. Lane 3: material immunoprecipitated using control IgG. Marked bands were excised from gel and subjected to analysis by mass spectrometry. Target molecular weight: 71.690.
- Submitter comment
- While the predicted size of Rad21 is ~72kD, according to product characterization literature (found at manufacturer's website), the bands at ~70kD are of unknown origin while a band of ~140kD, similar to the one observed here, is identified as Rad21. In support of this, siRNAs targeting Rad21 dramatically reduce levels of the 140kD band, while levels of the 70kD band are unaffected (see Figure 2 of this document). 1. Hyperphosphorylation (ref. PMID 11073952 & many others) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/gene/5885 2. Dimerisation as part of cohesin complex (whose other members we can detect in the 130kDa band, refs. PMIDs 23874961 & 19075111)
- Submitted by
- Nathaniel Watson
- Lab
- Michael Snyder, Stanford
- Grant
- U54HG006996
- Download
- Rad21_ab992.jpg
RAD21 (Homo sapiens)
Method: immunoprecipitation followed by mass spectrometry
not submitted for review by lab
- Caption
- IP followed by mass spectrometry. Briefly, protein was immunoprecipitated from K562 nuclear cell lysates using the antibody ab992, and the IP fraction was loaded on a 10% polyacrylamide gel (NuPAGEBis-Tris Gel) and separated with an Invitrogen NuPAGE electrophoresis system. The gel was stained by ColloidialCoomassie G-250 stain, gel fragments corresponding to the bands indicated were excised. Then proteins were trypsinized using the in-gel digestion method. Digested proteins were analyzed on an Orbitrap Elite mass spectrometer (Thermo Scientific) by the nanoLC-ESI-MS/MS technique. Peptides were identified by the SEQUEST algorithm and filtered with a high confidence threshold (Peptide false discovery rate < 1%, 2 unique peptides per protein minimum, mass error < 10 ppm).
- Submitter comment
- Band B: RAD21 peptides could not be detected, however siRNA treatment results in knockdown of Band B (see antibody lot ENCAB000AKG). Hyperphosphorylation of RAD21 or dimerisation as part of cohesin complex might result in a more stable version of the protein which couldn’t be fragmented during our mass spec analysis.
- Submitted by
- Nathaniel Watson
- Lab
- Michael Snyder, Stanford
- Grant
- U54HG006996
- Download
- Rad21_final.pdf