ENCAB493UWX
Antibody against Homo sapiens YBX1
Homo sapiens
K562
characterized to standards
Homo sapiens
MCF-7, GM12878, HepG2, HEK293T
characterized to standards with exemption
Homo sapiens
any cell type or tissue
partially characterized
- Status
- released
- Source (vendor)
- Bethyl Labs
- Product ID
- A303-230A
- Lot ID
- 1
- Characterized targets
- YBX1 (Homo sapiens)
- Host
- rabbit
- Clonality
- polyclonal
- Purification
- affinity
- Isotype
- IgG
- External resources
Characterizations
YBX1 (Homo sapiens)
K562
not compliant
- Caption
- Immunoprecipitation was performed on nuclear extracts from the cell line: K562, using the antibody A303-230A. The blot shows western blot analysis of input, flowthrough, immunoprecipitate and mock immunoprecipitate using IgG.
- Reviewer comment
- signal is in the IgG
- Submitted by
- Denis Salins
- Lab
- Michael Snyder, Stanford
- Grant
- U54HG006996
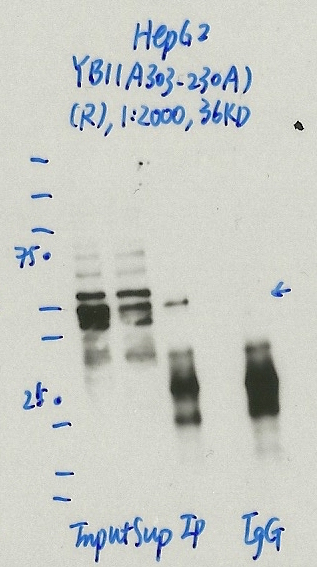
YBX1 (Homo sapiens)
HepG2
exempt from standards
- Caption
- Immunoprecipitation was performed on nuclear extracts from the cell line: HepG2, using the antibody A303-230A. The blot shows western blot analysis of input, flowthrough, immunoprecipitate and mock immunoprecipitate using IgG.Molecular Weight: 35.924
- Submitter comment
- We'd like an exemption for this characterization.
- Reviewer comment
- Not within 20% of expected size, but on 8/5/16, the size discrepancy was exempted by the antibody review panel because the mass spec in K562 detects the TF in a similarly sized band.
- Submitted by
- Denis Salins
- Lab
- Michael Snyder, Stanford
- Grant
- U54HG006996
- Download
- 1062_10_YB1_A303-230A_HepG2.jpg
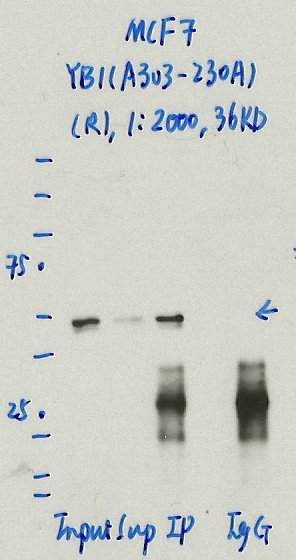
YBX1 (Homo sapiens)
MCF-7
exempt from standards
- Caption
- Immunoprecipitation was performed on nuclear extracts from the cell line: MCF-7, using the antibody A303-230A. The blot shows western blot analysis of input, flowthrough, immunoprecipitate and mock immunoprecipitate using IgG.Molecular Weight: 35.924
- Submitter comment
- Please exempt this characterization.
- Reviewer comment
- Not within 20% of expected size, but on 8/5/16, the size discrepancy was exempted by the antibody review panel because the mass spec in K562 detects the TF in a similarly sized band.
- Submitted by
- Denis Salins
- Lab
- Michael Snyder, Stanford
- Grant
- U54HG006996
- Download
- 1062_9_YB1_A303-230A_MCF7.jpg
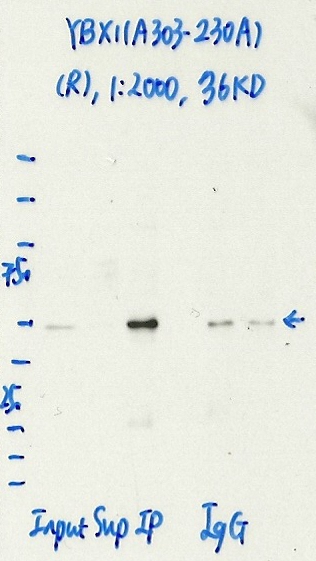
YBX1 (Homo sapiens)
K562
compliant
- Caption
- Immunoprecipitation was performed on nuclear extracts from the cell line: K562, using the antibody A303-230A. The blot shows western blot analysis of input, flowthrough, immunoprecipitate and mock immunoprecipitate using IgG.
- Submitted by
- Denis Salins
- Lab
- Michael Snyder, Stanford
- Grant
- U54HG006996
- Download
- 2_YB1(A303-230A).jpg
YBX1 (Homo sapiens)
not submitted for review by lab
- Caption
- IP-WB analysis of K562 whole cell lysate using YBX1 specific antibody. Lane 1 is 2.5% of 0.5mg input lysate, lane 2 is 2.5% of supernatant after immunoprecipitation and Lane 3 is 50% of IP enrichment using rabbit polyclonal anti-YB1. This antibody did not meet our primary validation criteria using our standard IP protocol in the indicated cell type.
- Submitted by
- Balaji Sundararaman
- Lab
- Gene Yeo, UCSD
- Grant
- U54HG007005
- Download
- Bethyl_A303-230A_1_YBX1.png
YBX1 (Homo sapiens)
GM12878
exempt from standards
- Caption
- Immunoprecipitation was performed on nuclear extracts from the cell line: GM12878, using the antibody A303-230A. The blot shows western blot analysis of input, flowthrough, immunoprecipitate and mock immunoprecipitate using IgG.Molecular Weight: 35.924
- Submitter comment
- Please exempt this characterization.
- Reviewer comment
- Not within 20% of expected size, but on 8/5/16, the size discrepancy was exempted by the antibody review panel because the mass spec in K562 detects the TF in a similarly sized band.
- Submitted by
- Denis Salins
- Lab
- Michael Snyder, Stanford
- Grant
- U54HG006996
- Download
- expt1063_5-YBX1-A303-230A.jpg
YBX1 (Homo sapiens)
HEK293T
exempt from standards
- Caption
- Immunoprecipitation was performed on nuclear extracts from the cell line: HEK293T, using the antibody A303-230A. The blot shows western blot analysis of input, flowthrough, immunoprecipitate and mock immunoprecipitate using IgG.Molecular Weight: 35.924
- Submitter comment
- The TF was detected in a similarly sized band in the K562 IP-MS characterization.
- Reviewer comment
- Not within 20% of expected size, but on 8/5/16, the size discrepancy was exempted by the antibody review panel because the mass spec in K562 detects the TF in a similarly sized band.
- Submitted by
- Nathaniel Watson
- Lab
- Michael Snyder, Stanford
- Grant
- U54HG006996
- Download
- Expt1113_4-YBX1-A303-230A.JPG
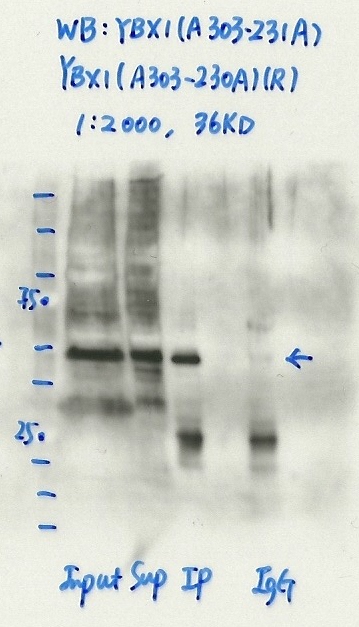
YBX1 (Homo sapiens)
K562
exempt from standards
- Caption
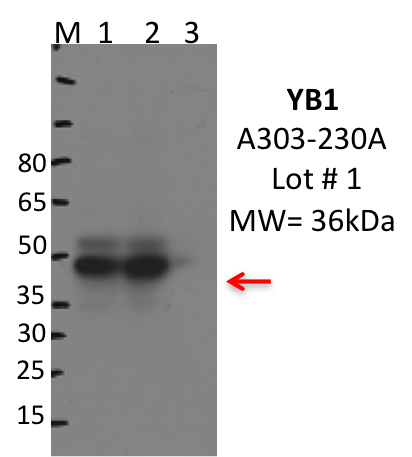
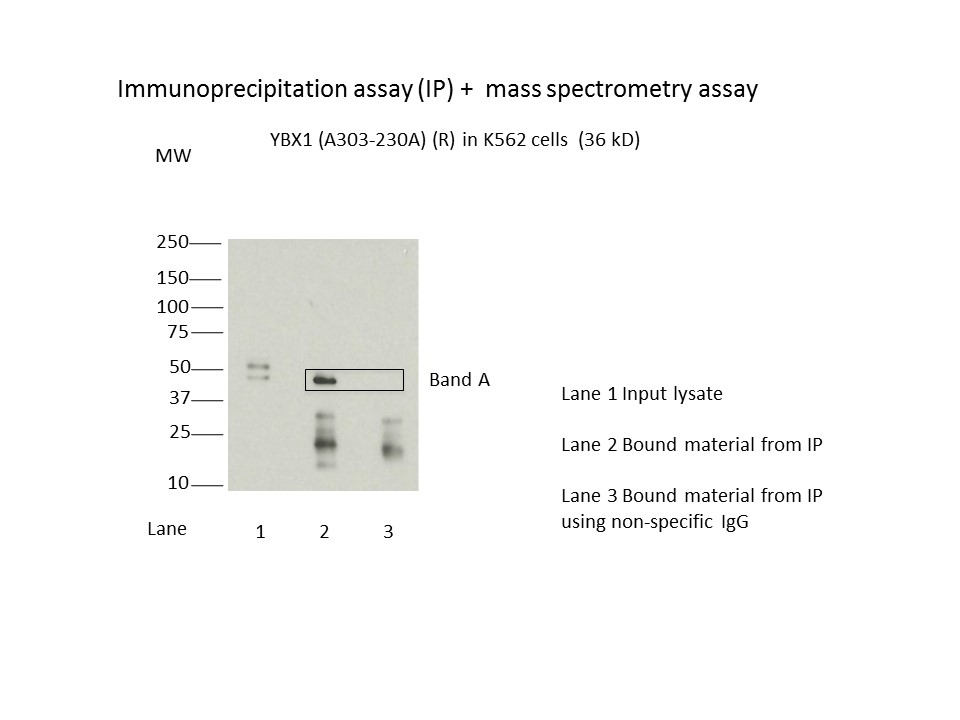
- Immunoprecipitation was performed on nuclear extracts from the cell line K562 using the antibody A303-230A. Lane 1: input nuclear lysate. Lane 2: material immunoprecipitated with antibody. Lane 3: material immunoprecipitated using control IgG. Marked bands were excised from gel and subjected to analysis by mass spectrometry. Target molecular weight: 35.924.
- Submitter comment
- --
- Reviewer comment
- Band is not within 20% of expected size, but rescued by mass spectrometry analysis
- Submitted by
- Nathaniel Watson
- Lab
- Michael Snyder, Stanford
- Grant
- U54HG006996
- Download
- YBX1.jpeg
YBX1 (Homo sapiens)
Method: immunoprecipitation followed by mass spectrometry
compliant
- Caption
- IP followed by mass spectrometry. Briefly, protein was immunoprecipitated from K562 nuclear cell lysates using the antibody A303-230A, and the IP fraction was loaded on a 10% polyacrylamide gel (NuPAGEBis-Tris Gel) and separated with an Invitrogen NuPAGE electrophoresis system. The gel was stained by ColloidialCoomassie G-250 stain, gel fragments corresponding to the bands indicated were excised. Then proteins were trypsinized using the in-gel digestion method. Digested proteins were analyzed on an Orbitrap Elite mass spectrometer (Thermo Scientific) by the nanoLC-ESI-MS/MS technique. Peptides were identified by the SEQUEST algorithm and filtered with a high confidence threshold (Peptide false discovery rate < 1%, 2 unique peptides per protein minimum, mass error < 10 ppm).
- Submitter comment
- None of the detected proteins are DNA-binding proteins
- Submitted by
- Nathaniel Watson
- Lab
- Michael Snyder, Stanford
- Grant
- U54HG006996
- Download
- YBX1_A303-230A Final.pdf