ENCAB000AER
Antibody against Homo sapiens JUN, Mus musculus JUN
Homo sapiens
K562
characterized to standards
Homo sapiens
MCF-7, A549
characterized to standards with exemption
Homo sapiens
any cell type or tissue
partially characterized
Mus musculus
any cell type or tissue
partially characterized
Homo sapiens
HeLa-S3
not characterized to standards
- Status
- released
- Source (vendor)
- Santa Cruz Biotech
- Product ID
- sc-1694
- Lot ID
- C2206
- Characterized targets
- JUN (Homo sapiens), JUN (Mus musculus)
- Host
- rabbit
- Clonality
- polyclonal
- Purification
- other
- Antigen description
- Amino acids 1-79 mapping at the N-terminus of c-Jun p39 of human origin.
- External resources
Characterizations
JUN (Homo sapiens)
MCF-7A549
exempt from standards
- Caption
- New primary characterizations are not required for cell lines MCF-7 and A549 as the banding pattern in K562 (https://www.encodeproject.org/antibody-characterizations/b8a9f7da-59b3-4994-8978-8c19294c4f11/) is the same when compared to ENCAB118DQK, a characterized lot of the same antibody (sc-1694), and also the same when compared to the banding pattern in MCF-7 (https://www.encodeproject.org/antibody-characterizations/9f7d6074-d319-40a7-8f6f-543d7466f6c7/) and A549 (https://www.encodeproject.org/antibody-characterizations/e6f7a4f3-f20c-4bf2-b465-0afd24436a7b/) in the other lot. The ENCODE Antibody Review panel exempted this antibody from further characterization in A549 and MCF-7 by transitive property, on 11/02/16.
- Submitter comment
- We ran out of this lot and purchased another (ENCAB118DQK) and repeated the IP in K562, MCF-7 and A549 but ChIPs were already done with this lot.
- Reviewer comment
- This antibody was exempted from primary characterization in MCF-7 and A549 by the ENCODE Antibody Review Panel on 11/02/16.
- Submitted by
- Jessika Adrian
- Lab
- Michael Snyder, Stanford
- Grant
- U54HG006996
- Download
- ENCAB000AER_primary.png
JUN (Homo sapiens)
Method: motif enrichment
compliant
- Caption
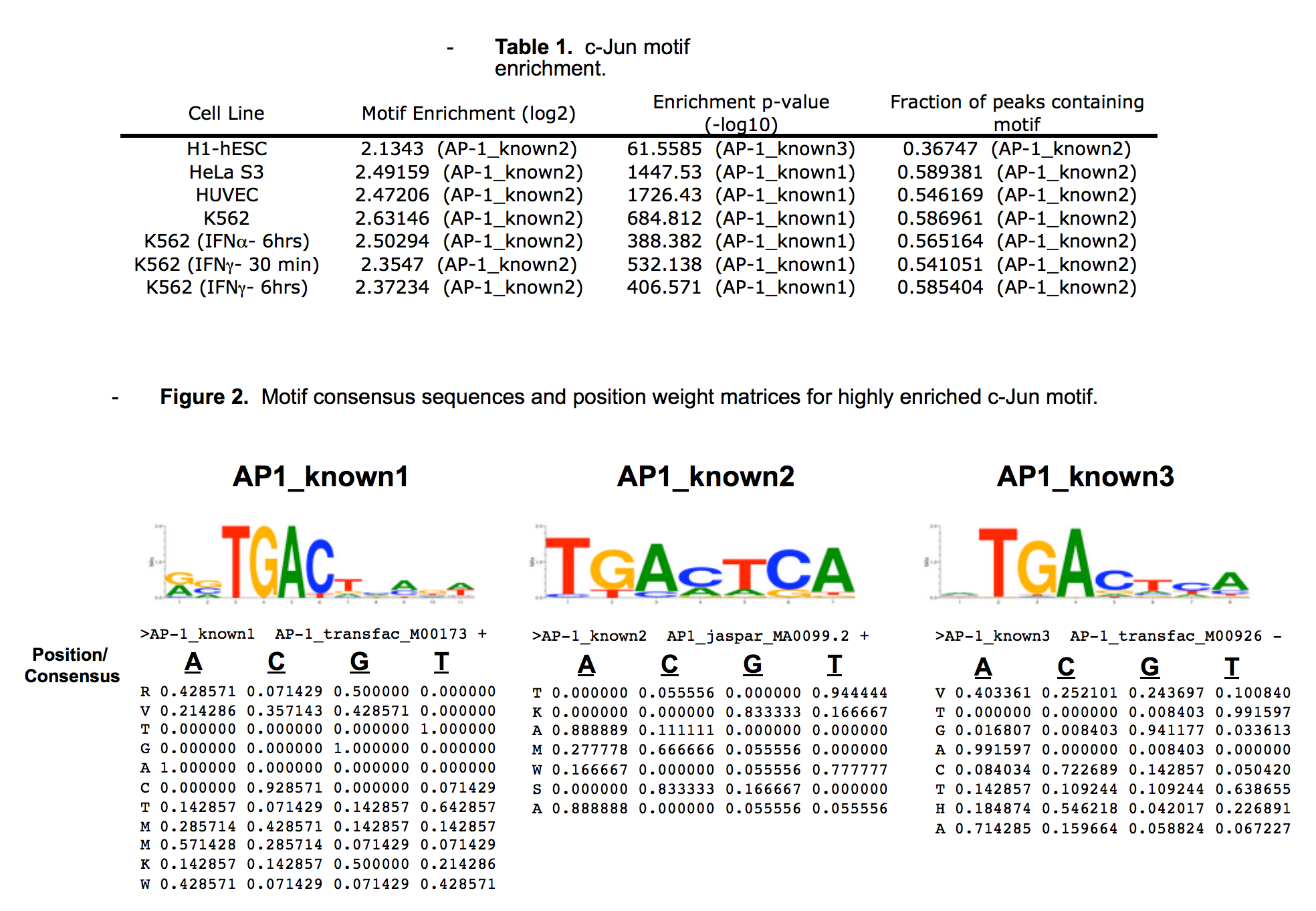
- The motif for target AP1 is represented by the attached position weight matrix (PWM) derived from ENCFF913JEG. Motif enrichment analysis was done by Dr. Zhizhuo Zhang (Broad Institute, Kellis Lab). Accept probability score: 0.828394775577 Global enrichment Z-score: 9.06154725688 Positional bias Z-score: 11.2528443659 Peak rank bias Z-score: 3.69771291138 Enrichment rank: 1.0
- Submitted by
- Kathrina Onate
- Lab
- Michael Snyder, Stanford
- Grant
- U54HG006996
JUN (Homo sapiens)
not reviewed
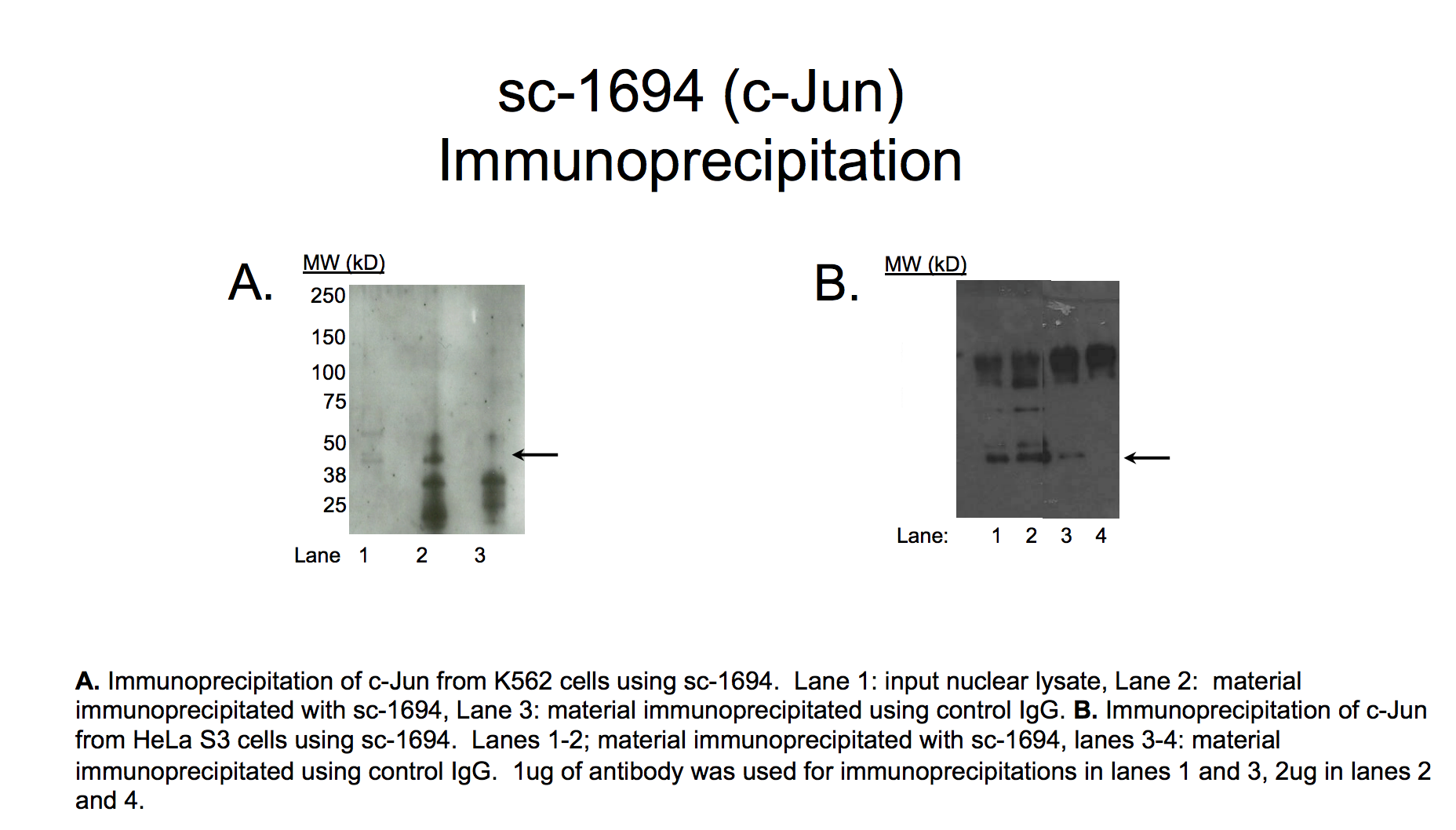
- Caption
- A major band with a mobility consistent with the size expected for c-Jun (~36kD; indicated by arrows) is specifically immunoprecipitated from nuclear lysates from K562 and HeLa S3 cells. Therefore, sc-1694 meets this criterion for validation.
- Submitted by
- Michael Snyder
- Lab
- Michael Snyder, Stanford
- Grant
- U54HG004558
- Download
- human_c-Jun_validation_Snyder-1.png
JUN (Homo sapiens)
not reviewed
- Caption
- Calculations were done by Pouya Kheradpour using a collection of known motifs available at http://www.broadinstitute.org/%7Epouyak/motif-disc/human/.Table 1 shows the fold-enrichments, enrichment p-values and fraction of peaks which contain the motif.The motif which produced the >largest value for each criterion is shown in Table 1.Note that while the maximally enriched motifs may differ from the motif with the highest enrichment p-values and the most represented motif, the motifs are highly similar (Figure 1) and thus all values are similar between motifs.Motifs were identified using a matching stringency corresponding to 4-6 (6-mer). Peaks identified by IDR (1% cutoff) were used in the analysis and +/-50bp from peak centers were considered. Enrichments are for a given motif vs. a background consisting of +/- 50bp from the centers of all DnaseI hypersensitive peaks.Repeat mask/simple repeats from UCSC and all gencode v7 exons (including non-protein coding genes) were excluded from the analysis.Comparison to shuffle motifs were used to correct for compositional bias.Enrichment is the corrected # of motifs in ChIP peaks/corrected # of motifs in DNaseI peaks.The current ENCODE standard calls for >4-fold enrichment and >10% motif representation for this criteria to be used for validation.The 7 c-Jun datasets presented here exceed these thresholds and sc-1694 is considered validated.
- Submitted by
- Michael Snyder
- Lab
- Michael Snyder, Stanford
- Grant
- U54HG004558
- Download
- human_c-Jun_validation_Snyder-2.png
JUN (Homo sapiens)
HeLa-S3HeLa-S3
not compliant
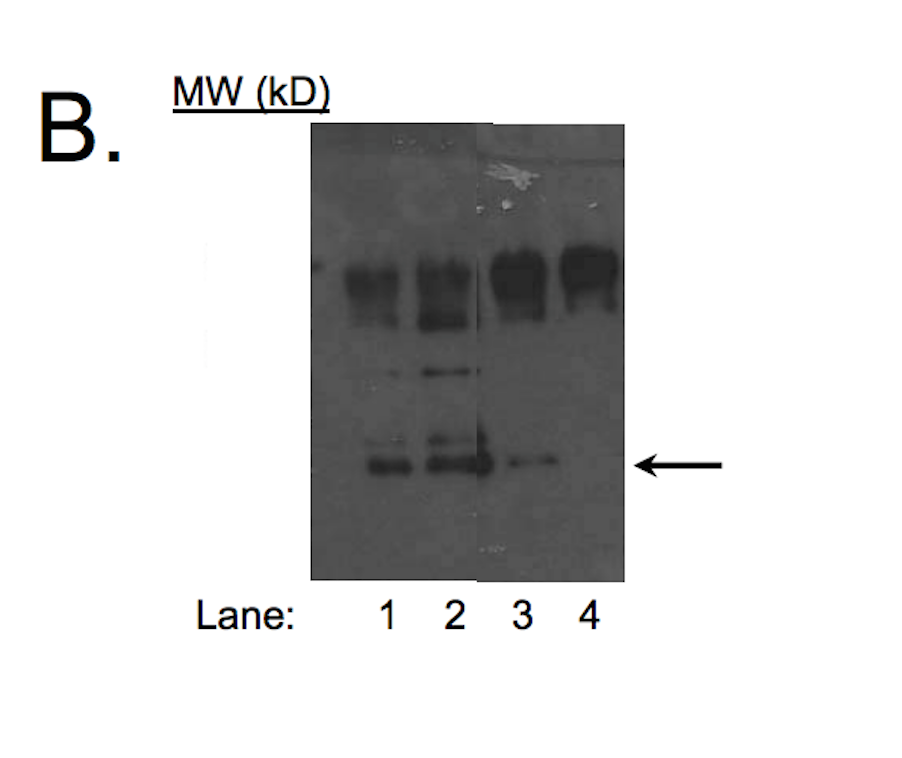
- Caption
- A major band with a mobility consistent with the size expected for c-Jun (~36kD; indicated by arrows) is specifically immunoprecipitated from nuclear lysate from HeLa-S3 cell line. Lanes 1-2: material immunoprecipitated with sc-1694. Lanes 3-4: material immunoprecipitated using control IgG. 1μg of antibody was used for immunoprecipitation in lanes 1 and 3; 2μg of antibody for lanes 2 and 4.
- Reviewer comment
- The submitting lab cannot find the original film so it's not possible to add a marker to interpret the size.
- Submitted by
- Kathrina Onate
- Lab
- Michael Snyder, Stanford
- Grant
- U54HG004558
- Download
- IP-HeLa-S3 Snyder AER.png
JUN (Homo sapiens)
K562
compliant
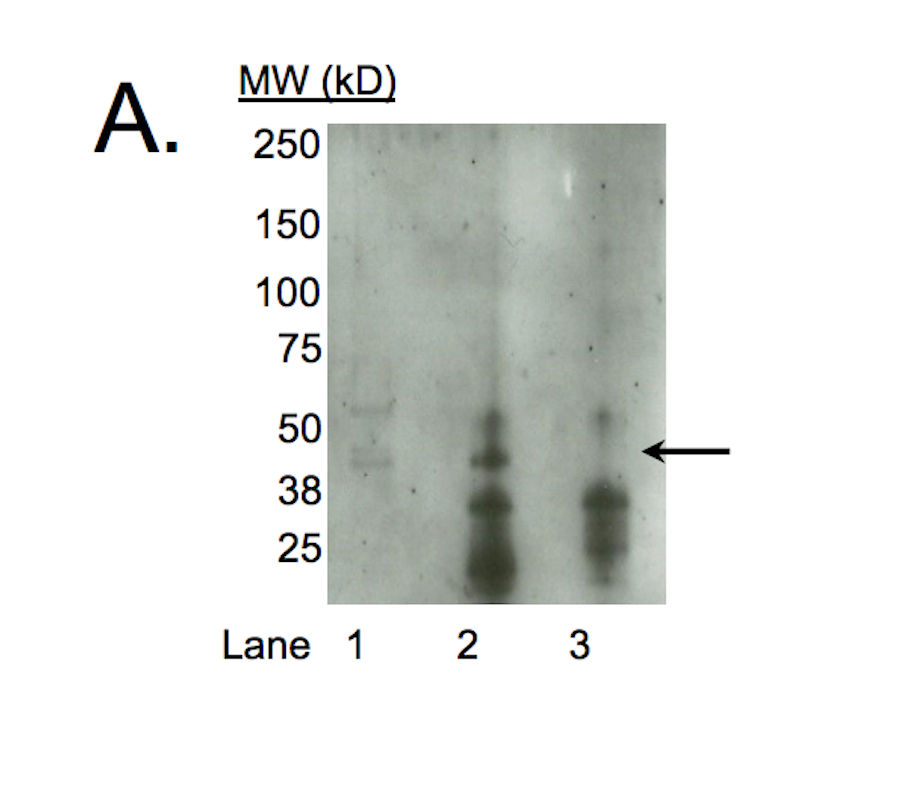
- Caption
- A major band with a mobility consistent with the size expected for c-Jun (~36kD; indicated by arrows) is specifically immunoprecipitated from nuclear lysate from K562 cell line. Lane 1: input nuclear lysate. Lane 2: material immunoprecipitated with sc-1694. Lane 3: material immunoprecipitated using control IgG.
- Submitted by
- Kathrina Onate
- Lab
- Michael Snyder, Stanford
- Grant
- U54HG004558
- Download
- IP-K562 Snyder AER.png
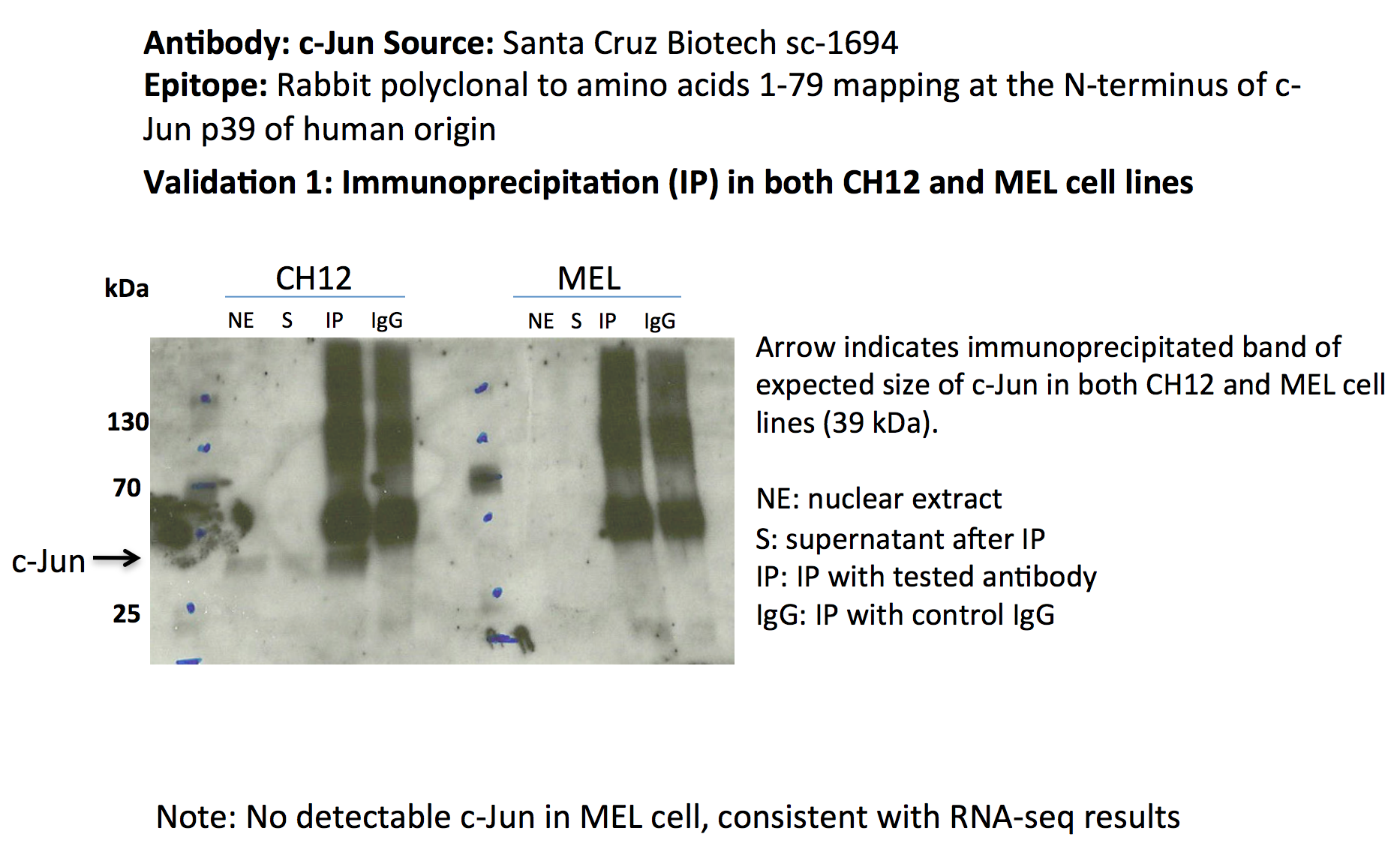
JUN (Mus musculus)
not reviewed
- Caption
- A band of ~39kD (expected size of c-Jun) is efficiently and specifically immunoprecipitated from CH12 lysates.
- Submitted by
- Michael Snyder
- Lab
- Michael Snyder, Stanford
- Grant
- RC2HG005602
- Download
- mouse_c-Jun_validation_Snyder-1.png